Tacsi, Kornélia and Stoffán, György Nimród and Galata, Dorián László and Pusztai, Éva and Gyürkés, Martin and Nagy, Brigitta and Szilágyi, Botond and Nagy, Zsombor Kristóf and Marosi, György and Pataki, Hajnalka (2023) Improvement of drug processability in a connected continuous crystallizer system using formulation additive. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICS, 635. No.-122725. ISSN 0378-5173
|
Text
Cikk3_improvementofdrug.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (7MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](http://real.mtak.hu/174555/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S037851732300145X-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (Graphical abstract (high resolution))
1-s2.0-S037851732300145X-ga1_lrg.jpg Download (256kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](http://real.mtak.hu/174555/8.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S037851732300145X-ga1.jpg)
|
Text (Graphical abstract (full size))
1-s2.0-S037851732300145X-ga1.jpg Download (31kB) | Preview |
Abstract
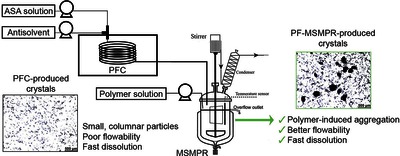
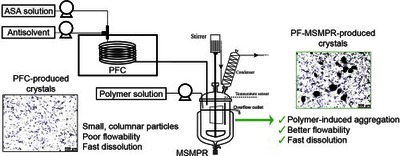
Continuous crystallization in the presence of polymer additives is a promising method to omit some drug formulation steps by improving the technological and also pharmacological properties of crystalline active ingredients. Accordingly, this study focuses on developing an additive-assisted continuous crystallization process using polyvinylpyrrolidone in a connected ultrasonicated plug flow crystallizer and an overflow mixed suspension mixed product removal (MSMPR) crystallizer system. We aimed to improve the flowability characteristics of small, columnar primary plug flow crystallizer-produced acetylsalicylic acid crystals as a model drug by promoting their agglomeration in MSMPR crystallizer with polyvinylpyrrolidone. The impact of the cooling antisolvent crystallization process parameters (temperature, polymer amount, total flow rate) on product quality and quantity was investigated. Finally, a spatially segmented antisolvent dosing method was also evaluated. The developed technology enabled the manufacture of purified, constant quality products in a short startup period, even with an 85% yield. We found that a higher polymer amount (7.5–14%) could facilitate agglomeration resulting in “good” flowability without altering the favorable dissolution characteristics of the primary particles.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Additional Information: | Funding Agency and Grant Number: National Research Development and Innovation Office of Hungary [K-143039, FK-132133, FK-143019, PD-142970, FK-138475]; Hungarian Academy of Sciences - National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary [2019-1.3.1 -KK -2019-00004, UNKP-22-3-II-BME-171, UNKP-22-4-II-BME-137, UNKP-22-5-BME-300]; New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund; Egis Pharmaceuticals PLC Funding text: This work was financially supported by the National Research Development and Innovation Office of Hungary (K-143039, FK-132133, FK-143019, PD-142970, FK-138475) . Hajnalka Pataki and Brigitta Nagy is thankful for the Janos Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. The research was funded by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary in the frame of the 2019-1.3.1 -KK -2019-00004 project. The research was also supported by the UNKP-22-3-II-BME-171, UNKP-22-4-II-BME-137 and UNKP-22-5-BME-300 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund. The authors thank Egis Pharma- ceuticals PLC for supporting the research with the overflow crystallizer device. |
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Continuous crystallizationDrug flowability improvementCrystallization additivesMixed suspension mixed product removalPlug flow crystallizerAcetylsalicylic acid reaction mixtureDesign of experiments |
| Subjects: | R Medicine / orvostudomány > RS Pharmacy and materia medica / gyógyszerészet, gyógyászati eszközök |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 23 Sep 2023 07:30 |
| Last Modified: | 23 Sep 2023 07:53 |
| URI: | http://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/174555 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |