Rónavári, Andrea and Ochirkhuyag, Altantuya and Igaz, Nóra and Szerencsés, Bettina and Ballai, Gergő and Huliák, Ildikó and Bocz, Csenge and Kovács, Ákos and Pfeiffer, Ilona and Csontné Kiricsi, Mónika and Kónya, Zoltán (2024) Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial and antitumor activity of MnOx nanoparticles. COLLOIDS AND SURFACES A : PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND ENGINEERING ASPECTS, 688. No.-133528. ISSN 0927-7757
|
Text
Q1_publication_Bolyai.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (3MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/204459/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0927775724003893-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
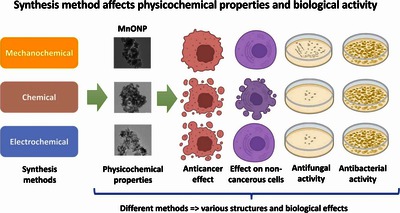
Text (graphical abstract)
1-s2.0-S0927775724003893-ga1_lrg.jpg Download (220kB) | Preview |
Abstract
Manganese oxide containing nanoparticles (MnOx NPs) have emerged as promising antimicrobial and anticancer agents due to their unique properties. However, the different initial materials and synthesis techniques often yield nanoparticles with highly different properties which limit their applications especially in the biomedical field. Thus, we aimed to explore the suitability of pyrolusite as a new and sustainable manganese mineral source for MnOx production. Moreover, we examined the effect of various synthesis methods on the physicochemical characteristics and biological activity of MnOx NPs to explore their therapeutic utilization potential against microbes and in cancer treatment. We produced MnOx NPs from a naturally occurring mineral via mechanochemical, chemical, and electrochemical processes, characterized them thoroughly, and assessed their cytotoxicity against bacteria, fungi, and human cancerous and non-cancerous cells. We verified that the synthesis method utilized to obtain MnOx NPs impacted significantly nanoparticle properties leading to distinct structural, morphological, and biological characteristics. Although none of the particles was effective against the tested bacterial strains, electrochemically produced NPs demonstrated significant antifungal activity. These nanoparticles were also the most potent anticancer agents, exhibiting cancer-selective toxicity attributed to apoptosis induction rather than altered cell proliferation or direct necrotic effects. These results are relevant for the development of effective and safe nanotherapeutics and highlight the potential of MnOx nanoparticles - obtained through carefully selected initial mineral source and adequate synthetic approach - in antimicrobial and anticancer therapy.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | MnOx NPs, nanoparticle synthesis,antimicrobial activity, antifungal activity, selective cytotoxicity, nanotherapeutics |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > Q1 Science (General) / természettudomány általában |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 07 Sep 2024 14:19 |
| Last Modified: | 07 Sep 2024 14:19 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/204459 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |