Augis, Luc and Nguyễn, Cảnh Hưng and Ciseran, Cécile and Wacha, András Ferenc and Mercier-Nomé, Françoise and Domenichini, Séverine and Sizun, Christina and Fourmentin, Sophie and Legrand, François-Xavier (2024) Hydrophobic binary mixtures containing amphotericin B as lipophilic solutions for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICS, 662. No.-124486. ISSN 0378-5173
|
Text
Augisetal.-2024-HydrophobicbinarymixturescontainingamphotericinBaslipophilicsolutionsforthetreatmentofc.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (5MB) | Preview |
|
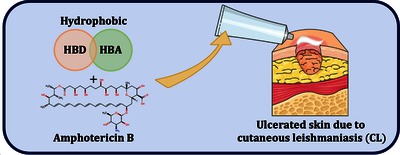
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/205792/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/graph%20abs.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
graph abs.jpg - Other Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (162kB) | Preview |
Abstract
Cutaneous leishmaniasis, caused by Leishmania parasites, requires treatments with fewer side effects than those currently available. The development of a topical solution based on amphotericin B (AmB) was pursued. The considerable interest in deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their remarkable advantages inspired the search for a suitable hydrophobic excipient. Various mixtures based on commonly used hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) and acceptors (HBAs) for DES preparations were explored. Initial physical and in-vitro screenings showed the potential of quaternary phosphonium salt-based mixtures. Through thermal analysis, it was determined that most of these mixtures did not exhibit eutectic behavior. X-ray scattering studies revealed a sponge-like nanoscale structure. The most promising formulation, based on a combination of trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride and 1-oleoyl-rac-glycerol, showed no deleterious effects through histological evaluation. AmB was fully solubilized at concentrations between 0.5 and 0.8 mg·mL−1, depending on the formulation. The monomeric state of AmB was observed by circular dichroism. In-vitro irritation tests demonstrated acceptable viability for AmB-based formulations up to 0.5 mg·mL−1. Additionally, an ex-vivo penetration study on pig ear skin revealed no transcutaneous passage, confirming AmB retention in healthy, unaffected skin.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Cutaneous leishmaniasis, Amphotericin B, Deep eutectic solvents, Low transition temperature mixtures, Lipophilic solution, MTT assay, Franz diffusion cells |
| Subjects: | R Medicine / orvostudomány > R1 Medicine (General) / orvostudomány általában |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 25 Sep 2024 07:35 |
| Last Modified: | 25 Sep 2024 07:35 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/205792 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |