Kecskés, Angéla and Czéh, Boldizsár and Kecskés, Miklós (2022) Mossy cells of the dentate gyrus: Drivers or inhibitors of epileptic seizures? BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA (BBA) - MOLECULAR CELL RESEARCH, 1869 (9). No.-119279.
|
Text
Kecskes_etal_2022.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (2MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/217055/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/gra.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
gra.jpg - Published Version Download (327kB) | Preview |
Abstract
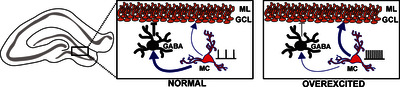
Mossy cells (MCs) are glutamatergic cells of the dentate gyrus with an important role in temporal lobe epilepsy. Under physiological conditions MCs can control both network excitations via direct synapses to granule cells and inhibition via connections to GABAergic interneurons innervating granule cells. In temporal lobe epilepsy mossy cell loss is one of the major hallmarks, but whether the surviving MCs drive or inhibit seizure initiation and generalization is still a debate. The aim of the present review is to summarize the latest findings on the role of mossy cells in healthy and overexcited hippocampus.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Epilepsy, Mossy cell, Granule cell, hippocampus, Dentate gyrus |
| Subjects: | R Medicine / orvostudomány > R1 Medicine (General) / orvostudomány általában > R850-854 Experimental medicine / kisérleti orvostudomány |
| Depositing User: | Angela Kecskes |
| Date Deposited: | 20 Mar 2025 07:53 |
| Last Modified: | 20 Mar 2025 07:53 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/217055 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |