Agbadua, Orinamhe Godwin and Kúsz, Norbert and Berkecz, Róbert and Vass, Elemér and Csámpai, Antal and Tóth, Gábor and Balogh, György Tibor and Marcourt, Laurence and Wolfender, Jean-Luc and Queiroz, Emerson Ferreira and Hunyadi, Attila (2025) New Insights into the French Paradox: Free Radical Scavenging by Resveratrol Yields Cardiovascular Protective Metabolites. JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, 68 (10). pp. 10031-10047. ISSN 0022-2623
|
Text
agbadua-et-al-2025-new-insights-into-the-french-paradox-free-radical-scavenging-by-resveratrol-yields-cardiovascular.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (4MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/219761/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/images_large_jm4c03061_0004.jpeg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
images_large_jm4c03061_0004.jpeg - Published Version Download (124kB) | Preview |
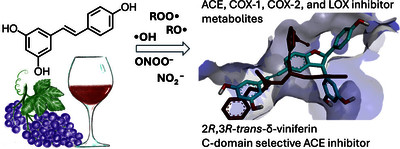
Abstract
Resveratrol was subjected to a diversity-oriented synthesis using oxidative transformations by various biorelevant, biomimetic, or biomimetic-related chemical reagents. Using a combined strategy of ultrahigh-resolution profiling, bioactivity screening, and bioactivity-guided isolation, 19 metabolites were obtained. The compounds were tested for their in vitro enzyme inhibitory activity on angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE), cyclooxygenase-1 and -2, and 15-lipoxygenase (LOX), and evaluated for their relevant drug-like properties in silico. The compounds demonstrated a generally increased cardiovascular protective and anti-inflammatory potential and better drug-likeness compared to resveratrol. Trans-δ-viniferin (6) was identified as a competitive, C-domain-selective ACE inhibitor that is over 20 times more potent than resveratrol. Further, trans-ϵ-viniferin (2) acted as an over 40 times stronger LOX inhibitor than resveratrol. While our results cannot be directly translated to the health benefits of dietary resveratrol consumption without further studies, it is demonstrated that biologically relevant oxidative environments transform resveratrol into potent cardiovascular protective and anti-inflammatory metabolites. © 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This work was funded by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office, Hungary (NRDIO; K134704 and TKP2021-EGA-32) by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology. M.V. was supported by the ÚNKP-23-4-222 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the Source of the NRDIO. |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > QD Chemistry / kémia R Medicine / orvostudomány > R1 Medicine (General) / orvostudomány általában |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 03 Jun 2025 14:32 |
| Last Modified: | 03 Jun 2025 14:32 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/219761 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |