Çok, Selay Sert and Koç, Fatos and Len, Adél and Almásy, László and Dudás, Zoltán Imre (2025) Silica aerogels modified with vinyl, epoxide, methacrylate moieties for the removal of ciprofloxacin by adsorption from water. SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGY, 354 (5). No-129112. ISSN 1383-5866
|
Text
2025-Cok-Sep-Pur-Tech.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (5MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/222464/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S138358662402851X-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
1-s2.0-S138358662402851X-ga1_lrg.jpg - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (226kB) | Preview |
Abstract
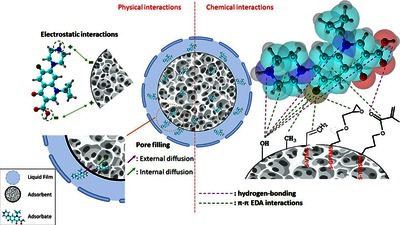
Water pollution caused by antibiotic effluents, particularly ciprofloxacin is a growing environmental concern. To address this problem, silica aerogels containing vinyl, epoxide, or methacrylate organic functionalities were synthesized through facile sol–gel synthesis under ambient conditions and employed as ciprofloxacin adsorbents in this study. The physicochemical and structural features of the materials were characterized using conventional and complementary techniques. Structural characterization confirmed the successful chemical functionalization of the silica surface for all samples. Similar to the pristine aerogel, the vinyl-functionalized aerogel displayed a typical mesoporous network, whereas epoxide and methacrylate functionalization caused dominantly macroporous structures. Batchwise sorption experiments were performed under different operating conditions. The results of the equilibrium and kinetic adsorption studies showed excellent alignment with the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models, respectively. Under optimum conditions (C0 = 100 mg/L, mads/Vsoln = 0.5, pH=6, t = 90 min), the adsorption capacities of ciprofloxacin onto vinyl, epoxide, and methacrylate-modified aerogels were 62.7, 45.8 and 47.8 mg/g, respectively. Despite of the differences at micro- meso- and macrostructure level, obtaining similar adsorptive performances confirms that mechanism of sorption is not only relied on pore filling but also controlled by molecular interactions. The adsorbents also exhibited repetable sorption performance for at least six cycles.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Functional silica aerogels, Ciprofloxacin, Antibiotic, Adsorption, Structure–activity relationship |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > QD Chemistry / kémia |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 19 Aug 2025 12:10 |
| Last Modified: | 19 Aug 2025 12:10 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/222464 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |