Kiss, Etelka and Bulátkó, Anna and Kozma, József and Homokiné Krafcsik, Olga and Kubinyi, Miklós and Kamarás, Katalin and Nagyné László, Krisztina (2025) Binding characteristics of fluorescent probes to pillararene modified graphene oxide nanosheets and their implications for indicator displacement assays. COLLOIDS AND SURFACES A : PHYSICOCHEMICAL AND ENGINEERING ASPECTS, 723. No.-137341. ISSN 0927-7757 (In Press)
|
Text
1-s2.0-S0927775725012440-main.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (7MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/224388/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0927775725012440-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
1-s2.0-S0927775725012440-ga1_lrg.jpg - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (173kB) | Preview |
Abstract
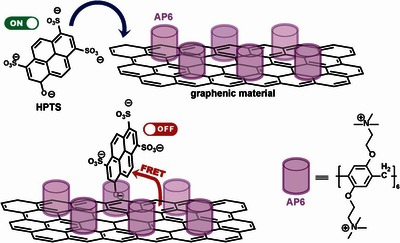
Fluorescent indicator displacement (FID) assays in which the macrocyclic host is grafted to a graphenic material have the advantage that they operate in turn-on mode, utilizing the FRET-type quenching of the graphenic component. As a contribution to the development of such sensors, we investigated the binding of a cationic and an anionic fluorescent probe, Oxazine 1 and Pyranine (HPTS) to a hybrid nanomaterial rGO-AP6 obtained by attaching a cationic pillar[6]arene (AP6) to reduced graphene oxide (rGO). The solid-state characteristics of this nanomaterial were unveiled using FT-IR, Raman and XP spectroscopy, while its properties in aqueous suspensions were investigated by UV-Vis, fluorescence and Zeta potential measurements. The binding of the two probes was investigated by adsorption studies at pH 6.4 and 10.2, using samples of low concentrations applicable in FID assays. It was found that rGO-AP6 binds HPTS strongly whereas the adsorption of OX is below the detection limit, which is opposite to the trend shown by the unmodified rGO adsorbent. The binding affinity of rGO-AP6 for HPTS could be tuned changing the pH. The AP6 units on the surface of rGO nanosheets proved to be closely homogenous binding sites for this anionic probe. These properties make the supramolecular system HPTS/rGO-AP6 a promising candidate as a fluorescent sensor for appropriate anionic biomolecules like ATP and other nucleotides. In general, the findings of this study underscore the considerable potential of modified rGO nanosheets as platforms for FID sensors.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Reduced graphene oxide, Fluorescence quenching, Adsorption, Fluorescent probe, FRET (Förster type resonance energy transfer), Electrostatic interactions |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > QD Chemistry / kémia |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 17 Sep 2025 06:33 |
| Last Modified: | 17 Sep 2025 06:33 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/224388 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |