Balogh, Csilla and Faragó, Nóra and Faludi, Tamás and Kovács, Zsófia and Kobak, Jarosław and Serfőző, Zoltán József (2025) Organic pollutants in a large shallow lake, and the potential of the local quagga mussel population for their removal. ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY, 296. No. 118201. ISSN 0147-6513
|
Text
BaloghCsEcotoxicology.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
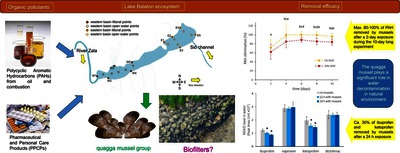
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/233502/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0147651325005378-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
1-s2.0-S0147651325005378-ga1_lrg.jpg - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (308kB) | Preview |
Abstract
Filter feeders, like mussels, can significantly lower the concentration of harmful substances in the water body. In the present study, we examined the distribution of organic pollutants (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [PAHs], non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]) in Lake Balaton, the largest shallow lake of Central Europe. We also investigated the sensitivity of the invasive quagga mussel to these substances and its potential to reduce their concentration in the water column. Our findings show that organic pollutant levels in Lake Balaton were generally below concentrations known to harm mussels, as indicated by the stress gene activity patterns observed along the lake’s longitudinal axis. However, in the most urbanized eastern part of the lake, especially in spring, we detected signs of environmental contamination from certain pollutants (e.g. diclofenac), highlighting potential risks to local ecosystems and communities. Removal capacity of the mussels for PAHs reached the maximum after four days of exposure to 5–10 % diluted water accommodated fraction of fuel-oil fraction #4 when the mussels (20 ind. L−1) reduced the PAH level by 100–85 %. Mussels (50 ind. L−1) removed 28 % and 21 % of ibuprofen and ketoprofen, respectively, from 1 µg L−1 concentrated solutions within 24 h. Many of the stress response genes were activated in the quagga mussel after their exposure to PAHs. These results suggest a significant role of gregarious invasive bivalves in the removal of organic pollutants from lake water.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Additional Information: | Export Date: 07 May 2025; Cited By: 0; Correspondence Address: Z. Serfőző; Tihany, BLKI, Klebelsberg Kuno street 3, H-8237, Hungary; email: serfozo.zoltan@blki.hun-ren.hu; CODEN: EESAD |
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, Organic pollutant, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, Quagga mussel, Shallow lake, Stress response gene |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > QH Natural history / természetrajz > QH301 Biology / biológia |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 08 Feb 2026 14:24 |
| Last Modified: | 08 Feb 2026 14:24 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/233502 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |