Ababneh, Haneen and Tóth, Andrea and Lente, Gréta and Balogh, Enikő and Csiki, Dávid Máté and Nagy, Béla and Szöőr, Árpád and Jeney, Viktória (2024) High phosphate and calcium induce osteoblastic phenotype switching and calcification of corneal epithelial cells in a Runx2-dependent and synergistic manner; a possible mechanism of chronic kidney disease-associated corneal calcification. BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-MOLECULAR BASIS OF DISEASE, 1870 (5). No.-167171. ISSN 0925-4439
|
Text
1-s2.0-S0925443924001601-main.pdf - Published Version Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (2MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/205739/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0925443924001601-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (Graphical Abstract)
1-s2.0-S0925443924001601-ga1_lrg.jpg - Other Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial. Download (203kB) | Preview |
Abstract
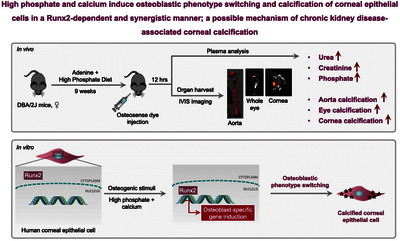
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) have elevated circulating calcium × phosphate product levels and exhibit soft tissue calcification. Besides the cardiovascular system, calcification is commonly observed in the cornea in CKD patients on hemodialysis. Cardiovascular calcification is a cell-mediated, highly regulated process, and we hypothesized that a similar regulatory mechanism is implicated in corneal calcification with the involvement of corneal epithelial cells (CECs). We established a mouse model of CKD-associated corneal calcification by inducing CKD in DBA/2J mice with an adenine and high phosphate diet. CKD was associated with aorta and corneal calcification as detected by OsteoSense staining and corneal Ca measurement (1.67-fold elevation, p < 0.001). In vitro, excess phosphate and Ca induced human CEC calcification in a dose-dependent and synergistic manner, without any influence on cell viability. High phosphate and Ca-containing osteogenic medium (OM; 2.5 mmol/L excess phosphate and 0.6 mmol/L excess Ca over control) increased the protein expression of Runx2 and induced its nuclear translocation. OM increased the expression of the bone-specific Ca-binding protein osteocalcin (130-fold increase, p < 0.001). Silencing of Runx2 attenuated OM-induced CEC calcification. Immunohistology revealed upregulation of Runx2 and overlapping between the Runx2 and the Alizarin red positive areas of calcification in the cornea of CKD mice. This work sheds light on the mechanism of CKD-induced corneal calcification and provides tools to test calcification inhibitors for the prevention of this detrimental process.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Subjects: | R Medicine / orvostudomány > R1 Medicine (General) / orvostudomány általában |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 24 Sep 2024 15:33 |
| Last Modified: | 24 Sep 2024 15:33 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/205739 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |