Casian-Plaza, Fernando A. and Palásti, Dávid J. and Schubert, Félix and Galbács, Gábor (2024) Optimization of nanoparticle-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the hyperspectral chemical mapping of solid samples. ANALYTICA CHIMICA ACTA, 1330. ISSN 0003-2670
|
Text
AnalyticalappsofNELIBSmappingACA2024.pdf - Published Version Download (6MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://real.mtak.hu/205944/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0003267024010705-ga1_lrg.jpg)
|
Text (graphical abstract)
1-s2.0-S0003267024010705-ga1_lrg.jpg - Published Version Download (498kB) | Preview |
Abstract
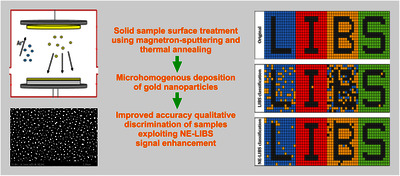
Background Nanoparticle-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (NE-LIBS) uses the plasmonic effect of metallic nanoparticles deposited on solid sample surfaces to achieve a significant signal enhancement by lowering the breakdown threshold and elevating plasma temperature. NE-LIBS has been used for localized analysis, but NE-LIBS mapping of solids has rarely been done, due to several challenges. In this study, we scrutinized the performance of NE-LIBS hyperspectral mapping of solid samples, when the controlled deposition of nanoparticles was done using magnetron sputtering. Results We performed a detailed optimization of the nanoparticle-related signal enhancement involving the laser wavelength, laser fluence and detector gating. It was confirmed that while the laser wavelength has only a small influence in the studied range (at 266 nm, 532 nm and 1064 nm), but there is an optimum for laser fluence and detection gate delay. The best signal enhancement achieved for a glass sample was 25–30. The applicability of the approach was demonstrated by hyperspectral NE-LIBS mapping of a granite rock sample, which provided an improved sensitivity in the study of the elemental distribution (exemplified for Li and Mg), and by paint linear discriminant analysis, in which NE-LIBS gave rise to a significantly improved accuracy (98 %, as opposed to the LIBS accuracy of only 84 %). Significance The analytical benefits of NE-LIBS hyperspectral mapping was demonstrated in two applications involving industrially relevant sample types. For example, the enhanced signals in rock elemental mapping can improve the localization of mineral grains viable for economic mining. The qualitative discrimination application involving paints demonstrates that the NE-LIBS approach can be beneficial in the spatial classification or identification of the local quality of a solid sample surface.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | Magnetron sputtering, Nanoparticle-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (NE-LIBS), Spatial classification, Qualitative discrimination |
| Subjects: | Q Science / természettudomány > QD Chemistry / kémia > QD01 Analytical chemistry / analitikai kémia |
| SWORD Depositor: | MTMT SWORD |
| Depositing User: | MTMT SWORD |
| Date Deposited: | 26 Sep 2024 09:23 |
| Last Modified: | 26 Sep 2025 23:15 |
| URI: | https://real.mtak.hu/id/eprint/205944 |
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |